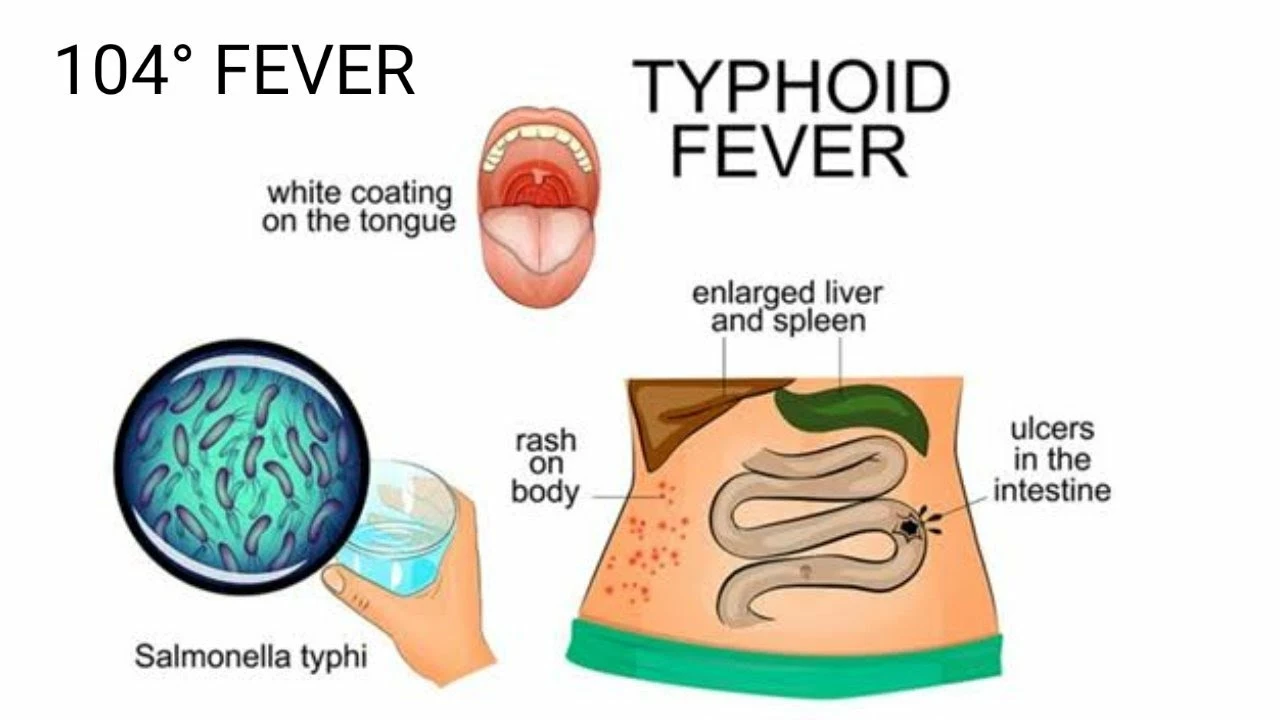
Understanding Typhoid Fever: Symptoms and Causes
Typhoid fever is a bacterial infection caused by the bacterium Salmonella Typhi. This illness is commonly transmitted through contaminated water or food and is especially prevalent in areas with poor sanitation facilities. Symptoms of typhoid fever may include high fever, headache, abdominal pain, and constipation or diarrhea. In some cases, patients may also experience a rash or an enlarged spleen. If left untreated, typhoid fever can lead to severe complications and even death.
As a blogger, it's essential for me to share valuable information about this disease, so my readers can take preventive measures and be aware of the available treatments. In this article, I will discuss the use of erythromycin for the treatment and prevention of typhoid fever, and why it's essential to consider this antibiotic as a viable option.
Erythromycin: An Overview of its Properties and Uses
Erythromycin is a macrolide antibiotic that has been used for decades to treat various bacterial infections. It works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria, ultimately leading to their destruction. Some of the common uses of erythromycin include treating respiratory infections, skin infections, and sexually transmitted diseases. In recent years, it has also been used as an alternative treatment for typhoid fever, especially in cases where the patient is allergic to other antibiotics or when the bacteria are resistant to traditional treatments.
While erythromycin is not the first-line treatment for typhoid fever, it's crucial to understand its potential benefits and how it can be used as an alternative therapy when other options fail.
Using Erythromycin to Treat Typhoid Fever
When it comes to treating typhoid fever, the first-line antibiotics are usually fluoroquinolones, such as ciprofloxacin, or cephalosporins, like ceftriaxone. However, in some cases, these antibiotics may not be effective due to resistance, or they may cause an allergic reaction. In such situations, erythromycin can be used as an alternative treatment option.
Erythromycin is typically administered orally, but it can also be given intravenously in severe cases. The dosage and duration of treatment depend on the severity of the infection and the patient's overall health. It's essential to follow the prescribed treatment plan to ensure the bacteria are completely eradicated and to prevent the development of antibiotic resistance.
Preventing Typhoid Fever with Erythromycin
While erythromycin is primarily used for treating active typhoid fever infections, it can also be used as a preventive measure in certain situations. For example, if someone has been exposed to the bacteria but has not yet developed symptoms, a short course of erythromycin may help prevent the onset of the illness.
Additionally, erythromycin can be used as a prophylactic measure for travelers visiting regions where typhoid fever is endemic. However, it's essential to note that taking erythromycin for prevention should not replace other preventive measures, such as getting vaccinated and practicing good hygiene while traveling.
Side Effects and Precautions with Erythromycin
Like any medication, erythromycin may cause side effects in some patients. Common side effects may include stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and loss of appetite. In rare cases, erythromycin may cause more severe side effects, such as irregular heartbeat, hearing loss, or an allergic reaction. If you experience any concerning side effects while taking erythromycin, it's essential to consult your healthcare provider immediately.
Furthermore, erythromycin may interact with other medications, so it's crucial to inform your doctor of any other drugs you are taking before starting treatment. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also consult their healthcare provider before using erythromycin, as this antibiotic can potentially cause harm to the unborn baby or pass through breast milk.
Conclusion: Erythromycin as an Alternative for Typhoid Fever Treatment and Prevention
In conclusion, erythromycin is a viable alternative for the treatment and prevention of typhoid fever in cases where traditional antibiotics are not effective or cause an allergic reaction. While it's essential to follow the prescribed treatment plan and be aware of potential side effects, erythromycin can be a life-saving medication for those suffering from this potentially severe illness.
As always, prevention is better than cure, so it's crucial to practice good hygiene, get vaccinated if traveling to endemic regions, and be knowledgeable about the available treatments to stay safe and healthy.
Suraj Midya
India must stand up for its people by insisting on clean water and proper sanitation, otherwise we are betraying our own citizens. The fight against typhoid is not just a medical issue but a moral one, and letting the disease spread is indefinately unacceptable. Erythromycin can help where other drugs fail, but it should be used responsibly, not as a free‑for‑all cure. Everyone should understand that prevention starts with community responsibility and government accountability.
ashish ghone
Hey there, great job covering a complex topic – it’s not easy to break down antibiotics for a broad audience 😊. I really appreciate how you walked us through the symptoms, treatment options, and even the preventive side of erythromycin; it shows a deep commitment to public health education. For anyone considering prophylaxis while traveling, remember to combine the short course of erythromycin with the recommended vaccination, because redundancy is key in safeguarding health. Also, staying hydrated and eating well‑cooked foods can dramatically cut down the risk of infection, which is a point many overlook. It’s also worth noting that monitoring for side effects such as stomach upset or mild diarrhea is critical; catching these early prevents more serious complications later on. Keep spreading this knowledge, and don’t forget to encourage your readers to consult a healthcare professional before starting any antibiotic regime, as personalized advice can make all the difference. Your thoroughness inspires confidence, and I’m confident that many will benefit from the actionable steps you’ve outlined 🙌.
steph carr
What a thorough overview! It’s encouraging to see the balance between treatment and prevention highlighted, especially for travelers from countries where typhoid is still prevalent. By promoting both vaccination and proper hygiene, we respect cultural differences while championing universal health standards. This kind of balanced information helps readers make informed decisions without feeling overwhelmed.
Vera Barnwell
Let me tell you, the story behind erythromycin isn’t just about a pill that kills bacteria; it’s a saga of corporate intrigue that the mainstream media refuses to discuss. For decades, big pharma has quietly pushed macrolides as the “safe” alternative, all the while manipulating clinical trial data to hide the real efficacy numbers. When resistance patterns shifted, they conveniently rebranded erythromycin as a “backup” rather than admitting their initial miscalculations. The truth is, many of the studies cited in public health guidelines were funded by the very manufacturers that stand to profit from increased prescriptions. Moreover, the fact that erythromycin is often prescribed to travelers without proper vaccination is a deliberate strategy to create dependency on their products. You’ll never hear the whistleblowers talk about how they were threatened into silence after exposing the hidden side‑effects that don’t make it into the glossy pamphlets. And let’s not ignore the subtle but pervasive influence of lobbyists who ensure that alternative treatments, like traditional herbal remedies, are kept off the official charts. In some countries, the government’s health agencies have been infiltrated by these interests, resulting in policies that favor drug sales over genuine preventive measures. The result is a cycle where patients are encouraged to take antibiotics prophylactically, which then fuels the very resistance that the medical community warns about. If you dig deeper, you’ll find that the data on erythromycin’s effectiveness against typhoid is far less robust than the headlines suggest. Many of the “success stories” are actually case reports with limited sample sizes, not large‑scale randomized trials. This is the classic playbook: hype a drug, sell it globally, and then blame the user when it fails. So, before you accept erythromycin as a viable prophylactic, ask yourself who benefits from that narrative and whether there’s a hidden agenda driving the recommendations you’re reading. The evidence is out there; you just have to look beyond the press releases and marketing brochures. Stay skeptical, stay informed, and don’t let the pharmaceutical giants dictate your health decisions.
David Ross
It’s wonderful to see a balanced discussion on both treatment and prevention,; the article successfully merges scientific facts with practical advice,; readers can appreciate the nuanced perspective,; moreover, the emphasis on hygiene, vaccination, and responsible antibiotic use promotes a holistic approach,; let’s continue to share such comprehensive information,; together we can foster healthier communities,; thank you for contributing to this important conversation.
Henry Seaton
We need simple steps: drink clean water get vaccine and use erythromycin only when a doctor says so.
Baby Thingie
While your moral stance is appreciated, the statement “indefinately” should be “definitely,” and “free‑for‑all” is better written as “free‑for‑all.” Accuracy in language reinforces credibility. 😊
Abby Elizabeth
OMG this is like the worst health drama ever!!!