Understanding Carbimazole and Its Effects on the Immune System
As someone who has been diagnosed with an overactive thyroid, I understand the importance of finding the right medication to manage my condition. One such medication is carbimazole, which is commonly prescribed to patients with hyperthyroidism. However, like all medications, carbimazole can have some side effects on our immune system. In this article, I will share my insights on carbimazole and its effects on the immune system, as well as discuss some tips for managing these side effects.
How Carbimazole Works in Treating Hyperthyroidism
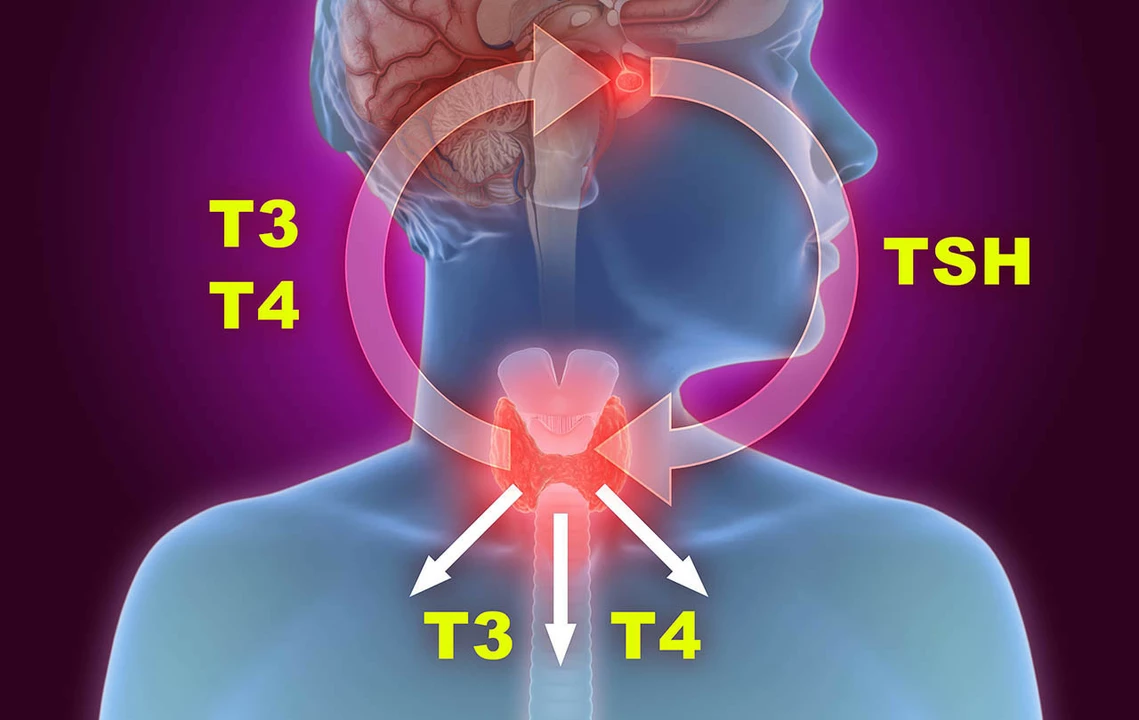
Before we delve into the effects of carbimazole on the immune system, it's essential to understand how this medication works in treating hyperthyroidism. Carbimazole is an antithyroid drug that inhibits the production of thyroid hormones by blocking the enzyme thyroid peroxidase. This enzyme is responsible for synthesizing thyroid hormones, which are essential for regulating our body's metabolism. By inhibiting this enzyme, carbimazole effectively reduces the levels of thyroid hormones in our body, helping to manage the symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
Carbimazole and Its Impact on the Immune System
While carbimazole is effective in treating hyperthyroidism, it can also have some adverse effects on our immune system. One of the most common side effects of carbimazole is a condition called agranulocytosis, which is characterized by a significant decrease in the number of white blood cells (specifically, neutrophils) in the body. Neutrophils are an essential part of our immune system, as they help fight off infections. When the number of neutrophils decreases, our bodies become more susceptible to infections, which can be potentially life-threatening.
Signs and Symptoms of Agranulocytosis
Since agranulocytosis is a significant concern when taking carbimazole, it's crucial to be aware of the signs and symptoms that may indicate this condition. Some of the most common symptoms of agranulocytosis include:
- Fever
- Chills
- Sore throat
- Mouth ulcers
- Swollen glands
- Unusual bleeding or bruising
- Fatigue
If you experience any of these symptoms while taking carbimazole, it's essential to contact your healthcare provider immediately, as agranulocytosis can be a medical emergency.
Monitoring Your Immune System While on Carbimazole
Given the potential risks to the immune system associated with carbimazole, it's essential to have regular blood tests to monitor your white blood cell count while taking this medication. Your healthcare provider will likely recommend frequent blood tests, especially during the first few months of treatment, to ensure that your white blood cell count remains within a safe range. If your blood tests show a significant decrease in your white blood cell count, your healthcare provider may adjust your carbimazole dosage or switch you to a different medication to manage your hyperthyroidism.
Preventing Infections While Taking Carbimazole
While on carbimazole, it's essential to take precautions to prevent infections, given the risk of agranulocytosis. Some preventive measures you can take include:
- Practicing good hand hygiene by washing your hands frequently with soap and water
- Avoiding contact with individuals who are sick or have contagious illnesses
- Getting vaccinated against common infections, such as the flu
- Maintaining a healthy diet to support your immune system
- Getting regular exercise to boost your immune function
By taking these precautions, you can help reduce your risk of infections while taking carbimazole.
Discussing Your Concerns with Your Healthcare Provider
As a patient taking carbimazole, it's crucial to maintain open communication with your healthcare provider about any concerns you may have regarding your immune system. Your healthcare provider will be able to provide guidance on managing the side effects of carbimazole and monitoring your immune system. If you experience any symptoms of agranulocytosis or have concerns about your immune function while taking carbimazole, don't hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider for advice and support.
Dean Briggs
Carbimazole, while a cornerstone in the management of hyperthyroidism, also invites a cascade of immunological considerations that merit deeper reflection.
When we examine the drug's mechanism, we notice its suppression of thyroid hormone synthesis, which indirectly modulates immune cell activity.
This modulation can be both a blessing and a curse, depending on the individual's baseline immune robustness.
In my experience, the subtle shift in neutrophil function often precedes the more overt signs of agranulocytosis.
The pathophysiology suggests that the drug may interfere with bone marrow granulation processes, leading to a quantitative dip in white blood cells.
Such a dip, though statistically rare, carries a weighty clinical significance because infections can accelerate rapidly in a compromised host.
Moreover, the psychological impact of living under the specter of a potential infection cannot be dismissed; anxiety itself can influence immune competence.
It is therefore prudent to adopt a holistic monitoring regimen that includes not only periodic complete blood counts but also lifestyle factors such as diet, sleep, and stress management.
Nutrient-rich foods, particularly those containing selenium and vitamin D, have been shown to support leukocyte function.
Regular, moderate exercise has a bidirectional effect, bolstering immune surveillance while avoiding the cortisol surge associated with overexertion.
Equally important is the role of vaccination; an annual flu shot can serve as a defensive buffer during the early months of therapy.
Patients should also be educated to recognize early warning signs such as sore throat or fever, because timely medical intervention can prevent catastrophic outcomes.
Some clinicians advocate for a staggered dose escalation, which may mitigate the abrupt impact on marrow activity.
In addition, interdisciplinary communication between endocrinologists and primary care providers ensures that any hematologic abnormality is promptly addressed.
Ultimately, the decision to continue carbimazole hinges on a risk-benefit analysis personalized to each patient, guided by vigilant monitoring and proactive self-care.
Sadie Speid
Carbimazole works by blocking thyroid peroxidase, which reduces hormone production.
This action helps bring thyroid levels back to normal, easing symptoms like tremors and weight loss.
However, the drug can occasionally lower neutrophil counts, increasing infection risk.
Regular blood tests every few weeks are essential during the first three months.
If you notice fever or a sore throat, contact your doctor right away.
Sue Ross
Feeling uneasy about a medication’s side effects is completely understandable.
Monitoring your white blood cell count can give you peace of mind while you adjust to carbimazole.
Remember that many people manage hyperthyroidism successfully with proper supervision.
Rohinii Pradhan
Carbimazole, an antithyroid pharmacologic agent, exerts its therapeutic efficacy through inhibition of thyroid peroxidase, thereby attenuating iodination of thyroglobulin.
Notwithstanding its clinical utility, the drug harbors a nontrivial propensity to precipitate agranulocytosis, a hematologic derangement of grave consequence.
It is incumbent upon clinicians to implement a regimented schedule of complete blood count assessments, particularly during the induction phase.
Patients should be apprised of cardinal signs such as pyrexia, odynophagia, and mucosal ulceration, which may herald leukopenic events.
Prophylactic measures, including stringent hand hygiene and avoidance of contagion, are advisable adjuncts to pharmacotherapy.
Anna-Lisa Hagley
Carbimazole’s risk profile is often downplayed, yet the data on agranulocytosis is stark.
Ignoring these warnings is a disservice to patient safety.
A Walton Smith
Just get your blood work done and call the doc if you feel sick.
Theunis Oliphant
In the grand tapestry of endocrine therapeutics, carbimazole occupies a paradoxical niche, simultaneously a savior and a potential harbinger of doom.
Its capacity to cripple neutrophil proliferation is not a trivial anecdote but a cornerstone of its pharmacodynamics.
One must therefore approach its prescription with the gravitas reserved for life‑altering interventions.
To eschew vigilance would be an act of professional negligence.
India Digerida Para Occidente
We must look beyond the textbook side‑effects and consider the holistic impact of carbimazole on daily living.
Regular monitoring is non‑negotiable, but so is maintaining a balanced diet rich in antioxidants.
Engaging with support groups can provide emotional resilience during the vulnerable early months.
Healthcare providers should personalize dosage adjustments rather than rely on a one‑size‑fits‑all protocol.
Only through collaborative effort can we mitigate risks while preserving therapeutic benefit.
Andrew Stevenson
From a clinical standpoint, carbimazole functions as a peroxidase inhibitor, curbing thyrotoxicosis by attenuating hormone synthesis.
The pharmacokinetic profile necessitates vigilant CBC monitoring to preempt neutropenia.
Early detection of agranulocytosis leverages the therapeutic window, allowing for rapid drug cessation.
Prophylactic stratagems, such as immunization against influenza, bolster patient resilience.
Patient education modules should emphasize symptomatology like odynophagia and unexplained febricity.
Ultimately, adherence to protocol optimizes outcome metrics.
Kate Taylor
I’ve seen a lot of patients on carbimazole who stay totally fine when they keep up with their labs.
It’s a good idea to set a reminder on your phone for those blood draws.
If you ever feel a sore throat or a fever, don’t wait-call your doctor ASAP.
Staying hydrated and eating a balanced diet can also help your immune system stay strong.
You’ve got this!
Hannah Mae
I don’t think everyone needs to be scared of carbimazole.
Sure, it can cause problems but most folks are ok.
Just keep an eye on it.
Iván Cañas
I echo the practical steps you outlined, Sadie, and would add that using a digital calendar can streamline the blood‑test schedule.
In addition, some patients find that a short course of vitamin B12 supplements supports overall marrow health, though evidence is mixed.
It’s also worthwhile to discuss dosage tapering with your endocrinologist once euthyroidism is achieved.
Keeping a symptom diary-especially noting any fevers or throat discomfort-can provide valuable data for your clinician.
This collaborative approach maximizes safety while preserving the drug’s therapeutic benefit.
Jen Basay
Interesting point about the risk, Anna‑Lisa. 😐 It’s true that agranulocytosis isn’t something to take lightly.
Patients often feel caught between the need for thyroid control and fear of side effects. 🌱
Hannah M
Your detailed explanation really clarifies the mechanism, Rohinii. 😊 Staying informed about signs like fever and sore throat is key.
I’ve heard that regular hand‑washing and avoiding sick contacts can lower infection risk. 👍
Poorni Joth
Yo Theunis, i get the drama but also the facts are clear.
Agranulocytosis is real, its not just a vague thing.
Keep the labs tight and talk to doc fast if you feel weird.
Dont ignore the signs.
Yareli Gonzalez
Andrew’s overview is thorough, and I would stress the importance of patient education on symptom recognition.
A calm, well‑structured plan for blood monitoring can reduce anxiety.
Support networks also play a valuable role.
Alisa Hayes
Your added tips about calendars and B12 are practical, Iván.
Consistency in tracking will pay off.
Mariana L Figueroa
Regular CBC checks are essential.
If you develop fever or sore throat act quickly.
Monitoring eases anxiety.
mausumi priyadarshini
Indeed, a balanced diet, regular exercise, and diligent monitoring, together form a comprehensive strategy, which cannot be overstated.
Carl Mitchel
Dean’s philosophical take captures the complexity of carbimazole therapy, but I would add that recent meta‑analyses suggest the incidence of agranulocytosis is lower than historically reported.
Moreover, genetic predispositions, such as HLA‑DRB1*08, have been linked to heightened risk, indicating a potential role for personalized screening.
Clinicians might also consider alternative thionamides like methimazole in specific scenarios, given its slightly different safety profile.
Ultimately, integrating pharmacogenomics with vigilant laboratory surveillance could refine risk stratification.
This balanced perspective aligns therapeutic efficacy with patient safety.