Understanding Leukemia and Its Treatment Options
As a blogger who is passionate about sharing information on health and medical topics, I am excited to discuss the role of radiation therapy in leukemia treatment. Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow, leading to the production of abnormal white blood cells. These abnormal cells can crowd out the healthy cells, making it difficult for the body to fight infections and function properly. There are several treatment options available for leukemia, including chemotherapy, targeted therapy, stem cell transplant, and radiation therapy. In this article, I will focus on radiation therapy and its role in treating leukemia.
The Science Behind Radiation Therapy
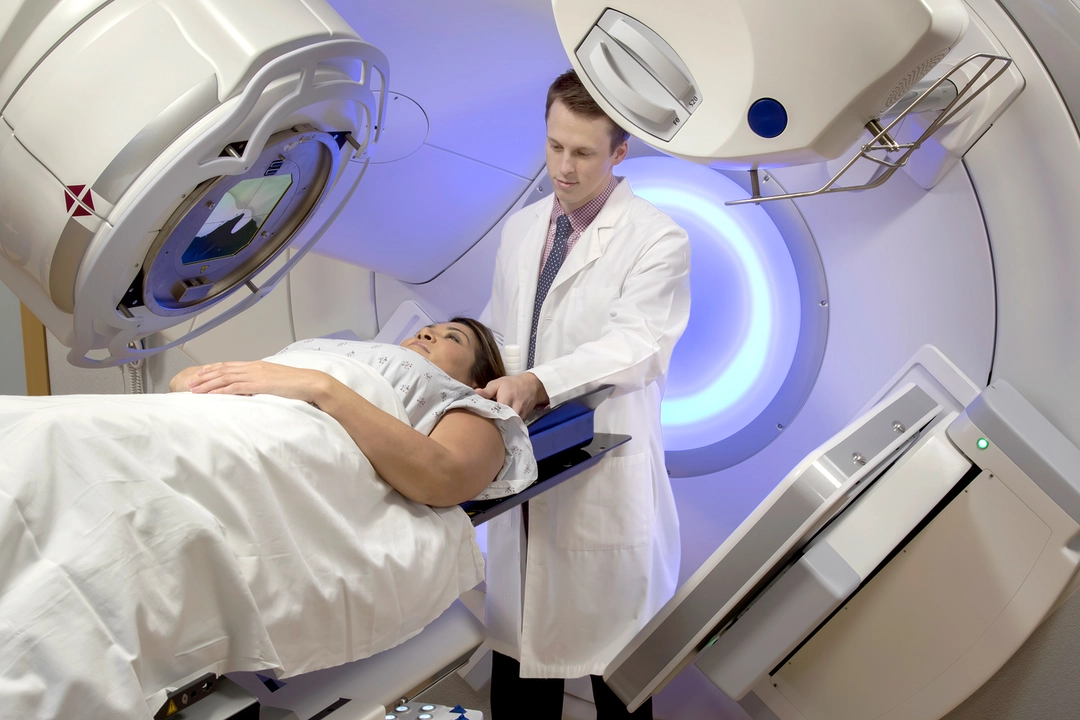
Radiation therapy is a cancer treatment that uses high-energy rays, such as x-rays or gamma rays, to destroy cancer cells. These rays can damage the DNA of cancer cells, preventing them from dividing and growing. Over time, this can help to shrink tumors and eliminate the cancerous cells from the body. Radiation therapy can be delivered through external beam radiation, where a machine directs the rays at the cancer site, or internal radiation, where a radioactive substance is placed inside the body near the cancer site.
When Is Radiation Therapy Used for Leukemia?
Radiation therapy may not be the primary treatment option for all types of leukemia, but it can play an important role in certain cases. It is often used in combination with other treatments, such as chemotherapy and stem cell transplants, to improve the overall outcome. Radiation therapy may be recommended for leukemia patients in the following situations:
- To treat a specific area of the body where leukemia cells have accumulated, such as the brain, spinal cord, or testicles.
- To prepare the body for a stem cell transplant by destroying any remaining cancer cells and suppressing the immune system, a process called total body irradiation (TBI).
- To relieve symptoms caused by leukemia, such as pain or swelling, in a process called palliative radiation therapy.
Total Body Irradiation: A Key Component of Stem Cell Transplantation
Total body irradiation (TBI) is a vital part of the stem cell transplant process for some leukemia patients. In TBI, radiation is used to destroy cancer cells throughout the entire body, including those that may be hidden in hard-to-reach areas. This helps to create space in the bone marrow for the new, healthy stem cells to grow and multiply. TBI also helps to suppress the patient's immune system, reducing the risk of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), a potentially serious complication of stem cell transplantation.
Side Effects of Radiation Therapy for Leukemia
As with any cancer treatment, radiation therapy can have side effects. Some of the most common side effects experienced by leukemia patients undergoing radiation therapy include:
- Fatigue
- Skin irritation, redness, or dryness at the radiation site
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Low blood cell counts, increasing the risk of infection, bruising, or bleeding
It is important to remember that not all patients will experience these side effects, and that they can often be managed with the help of a healthcare team.
Long-Term Effects and Follow-Up Care
While radiation therapy can be an effective treatment option for leukemia, it is essential to be aware of the potential long-term effects. Some patients may experience late side effects, which can occur months or even years after treatment has ended. These can include issues with growth and development in children, secondary cancers, or damage to organs such as the heart and lungs.
Regular follow-up care is crucial for leukemia patients who have undergone radiation therapy. This includes routine check-ups with healthcare providers, blood tests, and imaging studies to monitor for any signs of cancer recurrence or late side effects. It is also essential to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking, to help reduce the risk of long-term complications.
Conclusion: The Role of Radiation Therapy in Leukemia Treatment
In conclusion, radiation therapy can play a significant role in the treatment of leukemia, particularly when used in combination with other therapies such as chemotherapy and stem cell transplantation. By understanding the benefits and potential side effects of radiation therapy, patients and their families can make informed decisions about their treatment options and work closely with their healthcare team to achieve the best possible outcome.
HARI PRASATH PRASATH
Radiation therapy isn’t just a footnote in leukemia care; it’s a strategic weapon.
The article glosses over the nuanced dosimetry required for total body irradiation, which many clinicians overlook.
Andrew Miller
Another reminder that every cancer battle feels like a silent scream.
Brent Herr
The medical community has a moral obligation to be transparent about the risks of radiation therapy.
Too often they sugar‑coat the side effects as merely 'manageable'.
Patients deserve to know that total body irradiation can permanently damage healthy tissue.
This is not a trivial inconvenience; it can lead to secondary malignancies years later.
When doctors push radiation as a first‑line option without discussing alternatives, they betray trust.
They must present chemotherapy, targeted agents, and immunotherapy on equal footing.
Blindly following protocols without individualized assessment is ethically questionable.
Moreover, the socioeconomic barriers to accessing proper follow‑up care exacerbate inequities.
A low‑income family cannot afford frequent blood tests and imaging after treatment.
The system should fund comprehensive survivorship programs, not leave patients to fumble in the dark.
Radiation oncologists should undergo rigorous ethical training to balance cure versus harm.
Informed consent must include realistic statistics on long‑term organ toxicity.
The article could have highlighted these consent issues instead of merely listing side effects.
We should advocate for patient‑centered decision making, where preferences shape the treatment plan.
Only then can we claim to be advancing oncology responsibly.
Julius Adebowale
Data shows radiation outcomes vary; article oversimplifies.
KISHORE KANKIPATI
Wow, that was a fire‑storm of insight! 🌈 While I totally get the caution about side effects, I also think radiation can be a lifesaver when paired perfectly with chemo and a solid transplant plan.
Imagine a symphony where each instrument-chemo, targeted drugs, radiation-plays its part, creating a harmonious cure.
It’s all about balance, and the article does a decent job of laying out the basics.
Let’s keep the conversation bright and hopeful.
Jefferson Vine
Hold on-did you know that the push for radiation therapy is not just about patient outcomes? Big pharma and equipment manufacturers have a vested interest in keeping the market for linear accelerators alive. They fund research, sponsor conferences, and quietly influence guidelines, ensuring that radiation stays in the frontline arsenal. Meanwhile, emerging therapies like CAR‑T cells are being sidelined because they threaten huge profit streams. It’s a classic case of profit over patients, hidden behind glossy journal articles. The statistics you mentioned about side effects are carefully curated to downplay long‑term risks, keeping the public complacent. If you dig deeper, you’ll find whistleblowers who have spoken out about suppressed data on secondary cancers. The whole narrative is a staged performance, and we need to demand transparency. So next time you read a piece on leukemia treatment, ask yourself who’s really writing the script.
Ben Wyatt
Great points all around! For anyone considering radiation as part of a leukemia regimen, here’s what helps: work with a multidisciplinary team, keep a detailed symptom diary, and stay on top of blood counts.
Nutrition and gentle exercise can mitigate fatigue, and speaking with a radiation therapist about skin care can reduce irritation.
If you’re worried about long‑term effects, ask about modern techniques like intensity‑modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) that spare healthy tissue.
Regular follow‑up visits are key, and many centers now offer survivorship clinics that monitor late effects.
Remember, many patients successfully undergo total body irradiation and go on to thrive, especially with modern supportive care.
Stay hopeful and keep asking questions-you’re your own best advocate.